Global Recycling Day: 7 Ways GIS Impacts Current Recycling Initiatives
 0 min
0 minEvery year, March 18th marks Global Recycling Day, a worldwide focal point for promoting sustainable waste management. The combination of GIS and current knowledge around recycling practices offers a powerful unity to increased environmental consciousness. Let's explore how these two amplify the impact of recycling initiatives worldwide.

GIS: A Spatial Lens for Sustainability
At the heart of GIS lies the ability to capture, analyze, and visualize spatial data. In the context of recycling, GIS becomes a valuable tool for understanding the dynamics of waste generation, collection, and recycling infrastructure. Here's how GIS enhances the goals of Global Recycling Day:
Waste Stream Analysis:
GIS helps organizations conduct comprehensive waste stream analyses. By mapping the distribution of waste generation, authorities can identify hotspots, optimize collection routes, and implement targeted recycling campaigns.
Optimizing Recycling Centers:
GIS aids in the optimal placement of recycling centers. By considering factors such as population density, transportation networks, and accessibility, GIS ensures that recycling facilities are strategically located for maximum impact.
Community Engagement:
GIS maps have become powerful tools for community engagement. Visualizing recycling statistics and highlighting the impact of local initiatives fosters awareness and encourages residents to participate in recycling programs actively.
Monitoring and Reporting:
GIS platforms enable real-time monitoring of recycling activities. Municipalities and organizations can track the efficiency of their recycling programs, identify areas that need improvement, and generate insightful reports for stakeholders.
Route Optimization in Waste Collection:
GIS algorithms optimize waste collection routes, reducing fuel consumption and minimizing the environmental footprint of collection vehicles. This efficiency contributes to the overall sustainability of recycling programs.
Mapping Recycling Infrastructure:
GIS maps provide a comprehensive view of recycling infrastructure, including the location of recycling bins, drop-off points, and processing facilities. This information allows for better resource allocation and planning.
Waste Composition Analysis:
GIS supports waste composition studies, helping authorities understand the types of materials in the waste stream. This understanding guides recycling initiatives, directing efforts toward specific materials that need to be diverted from landfills.
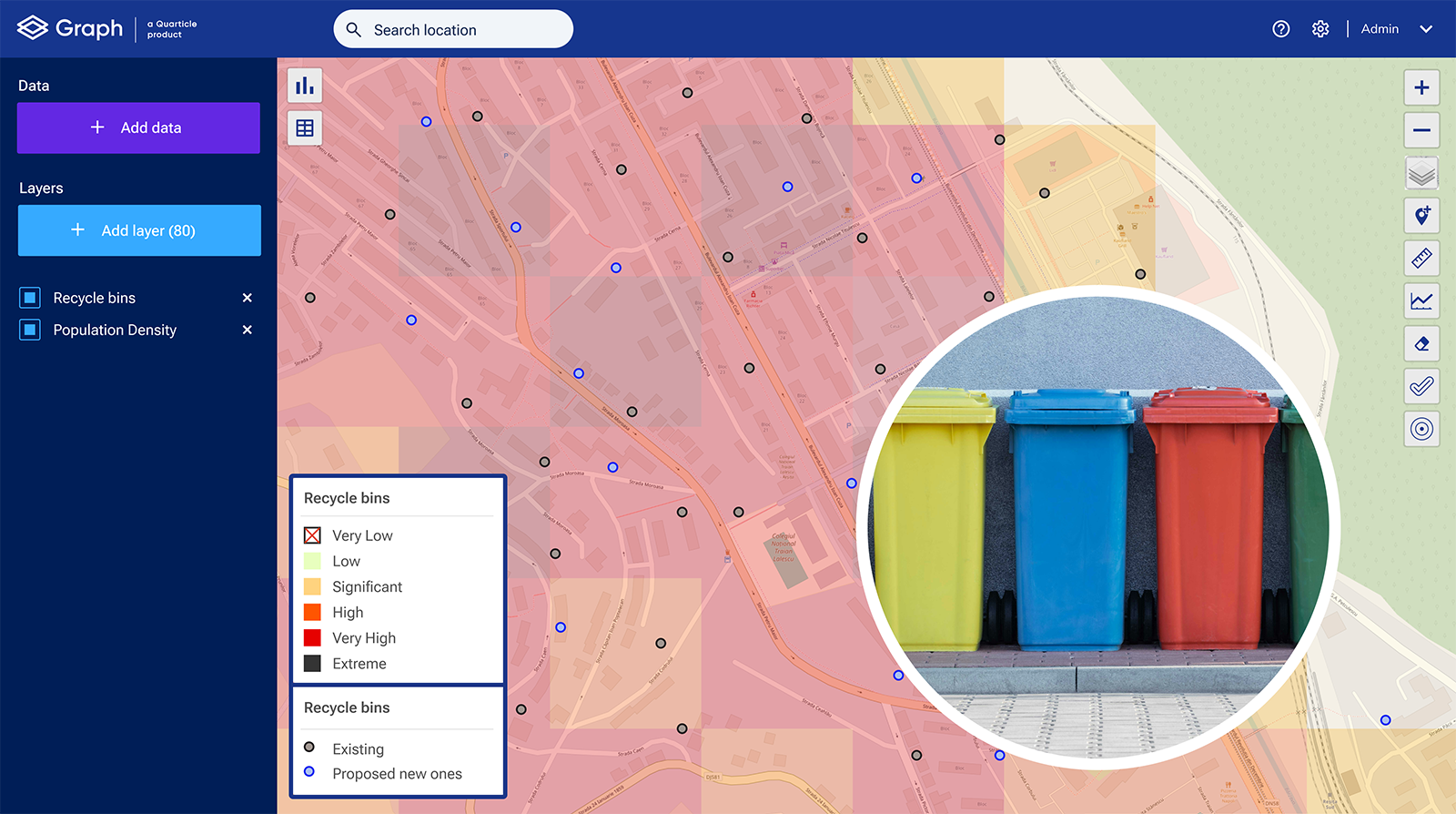
Using Graph you can see where new recycle bins need to be placed
As we celebrate Global Recycling Day, we acknowledge that GIS integration into recycling initiatives is a key component for mapping a sustainable tomorrow. By leveraging spatial intelligence, we enhance our ability to make informed decisions, optimize resources, and engage communities in the global pursuit of a greener tomorrow.
If you want to get a deeper understanding of what GIS is and how it can help you, check out our blog post page.