Demystifying GIS: Unlocking the Power of Location
 0 min
0 minHave you heard of GIS? Are you confused when it comes to understanding GIS? Do you know how to harness its power and make a long-lasting impact in your company?
In this article you will learn:
- What GIS stands for
- What is GIS used for
- How does GIS work
- 5 reasons why GIS is important for businesses today
What is GIS
A geographic information system (GIS) is a software system used for capturing, organizing (or reorganizing), processing, checking, storing, and visualizing spatial data (data related to placements on the Earth’s surface). The prefix Geo (coming from Greek) means earth or space. Simply put, GIS is the intersection of location and data. GIS encapsulates a full IT system, mainly software, hardware, and data.
How is GIS used?
GIS is extensively used in our day-to-day life, whether we are viewing and analyzing the buildings on a street, a building complex, or a scenic landscape (this type of data can be easily shown on a map in various map “layers”).
There is a large variety of information that can be analyzed by using GIS. This includes
- Population data, such as density, income, or education level
- Landscape data such as the specific locations of water & streams, variety of greenery and foliage, soil, etc.
- Different sites such as industrial sites, factories, farms, schools, or storm drains, road infrastructure (including bridges or tunnels), as well as electric power lines grids. Take a look at our blog post showcasing how GIS can prevent power line damage caused by severe weather conditions.
But GIS is more than just viewing and overlaying data. For example, by correlating the appropriate information, we can see if a new location for a factory is at risk of flood, hurricanes, earthquakes, and other natural catastrophes. These types of analysis support informed decision-making and help businesses assess risks.
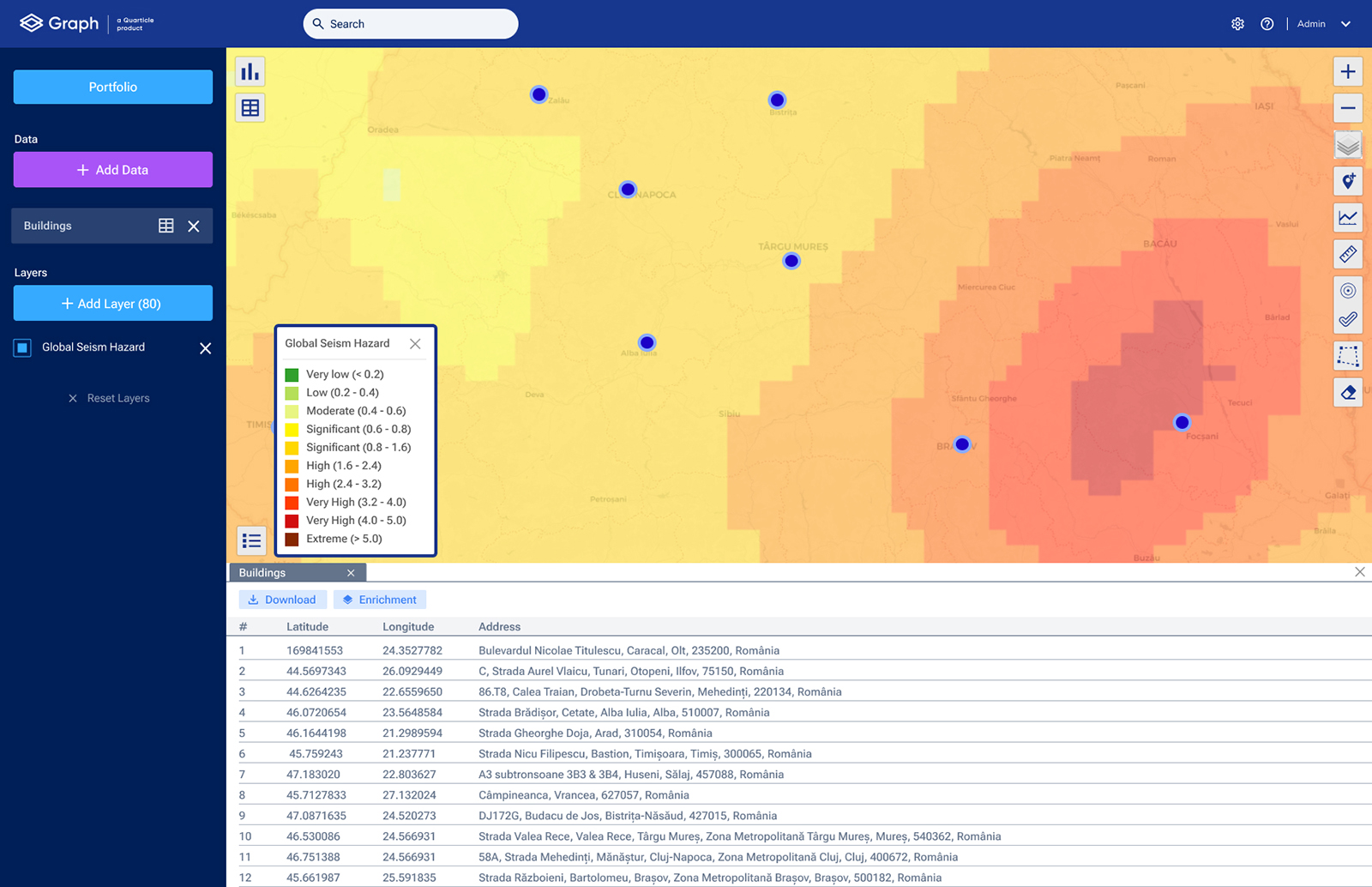
Example of Global Seism Hazard analysis in Graph by Quarticle
GIS can be specifically adapted and used in areas including
- Business
- Public and State Administration
- Science
- Everyday life (general public)
- Military
By linking and making sense of apparently unrelated data, GIS supports individuals and organizations in better understanding spatial patterns and relationships.
How does GIS work?
Let’s use a street map as an example. On a street map, you can find its name, geographic location, and intersections with other streets in the area. We then have the buildings on each side of the street, including private properties, commercial and office buildings, and other constructions. In addition to this, we have underground utilities like sewer pipes and gas pipes underneath the buildings and power cables above the ground. If we add the foliage and vegetation we end up with a complex map that is almost unreadable due to the large amount of information.
Everything that was added to the street map is location-based data. While in the past, standard maps could only display 1 or 2 datasets before becoming hard to use and understand, nowadays with the use of GIS, multiple datasets can be displayed on the map in a variety of separate layers. Predictions and proper planning can be done by analyzing spatial relations between the layers.
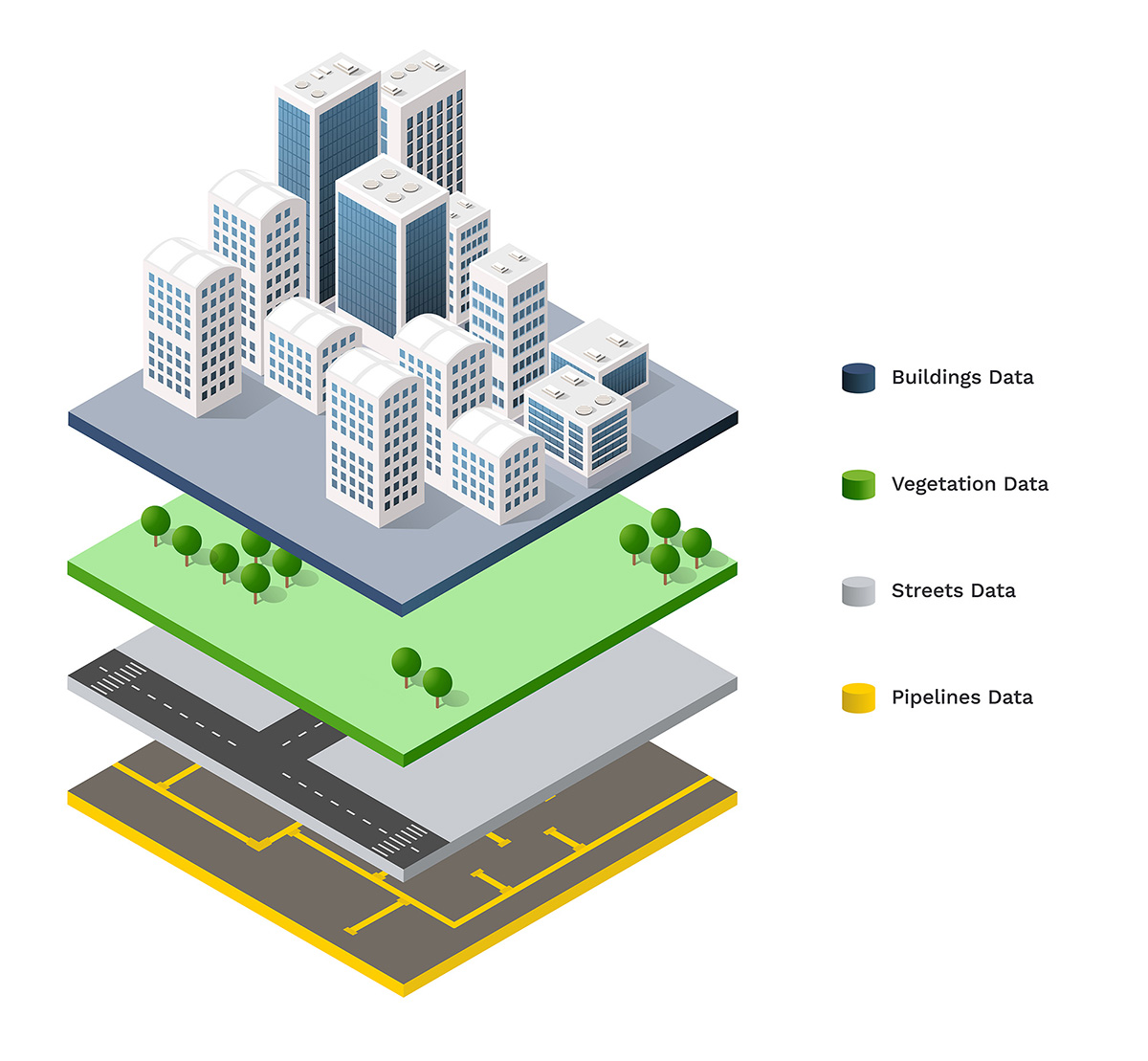
A GIS could also be called an interactive map enriched with different functions.
The information layers are made up of data and can be filtered or combined. The layers and locations on the map are visual and easier to use compared to sheets and tables. One example could be insurance companies seeing the distribution of their customers by the location of policies issued. By using GIS and a proper location intelligence application, underwriters can immediately see the areas that have lower or larger numbers of insured properties.
As mentioned previously, GIS applications include data, hardware, and software systems.
Data
GIS applications can include cartographic, photographic, and digital data, or data existing in spreadsheets.
Cartographic data already exists in map form, and can include location information for rivers, roads, hills, and valleys but can also include survey data and mapping information that can be entered directly into a software platform. Photographic interpretation is a significant part of GIS and involves analyzing aerial photographs and assessing the features that appear in them, such as computer data collected by satellites that show land use — the location of farms, towns, and forests.
Remote sensing provides another tool that can be integrated into a GIS. This includes images and other data collected from satellites, air balloons, and drones.
Finally, GIS can include data in tables or spreadsheets that relate to population demographics (from age, income, and ethnicity to recent purchases and internet browsing preferences).
GIS technology allows all these different types of information to be combined and used independently of their source or original format, using location as the key index variable that connects unrelated data.
Software
One of the basic functionalities of GIS software is geocoding. For data to be visualized on the map, it must be assigned a pair of coordinates (longitude, latitude). GIS software allows for large amounts of addresses to be geocoded fast, and be used immediately. Modern GIS tools run in a browser (can also be used on the go on a tablet) and are easy to use by a variety of stakeholders in the company (not just GIS experts).
Part of the software is also the know-how or methodology. Even if frequent standardized tasks can be done by a push of a button by non-GIS experts, complex problems require specific expertise from software developers, GIS specialists, and strategists. These experts have a variety of competencies including cloud computing, software development, DevOps, data analytics, and data science.
Hardware
When it comes to hardware, companies need to decide whether they want to operate the hardware themselves or use online services. A WebGIS runs in the browser, while the data and the software work in the cloud. Many geodata services are offered completely online. It’s up to each business to decide whether they want to use the cloud or their hardware.
5 reasons why GIS is important for companies today
Leaders across various industries use geoinformation and location intelligence to better understand which areas of their business are lacking crucial insights. To remove blind spots, find impactful solutions, and deliver business value, an extensive analysis is needed, but results have to be delivered fast and efficiently.
The reasons why a company should harness the power of GIS now are:
- By using GIS software you recognize hidden patterns at a glance that would otherwise be hidden in spreadsheets and tables
- Through GIS analysis you make faster and more accurate decisions in an objective way supported by data
- GIS software is more efficient than other methods resulting in cost reduction and cost optimization
- GIS can be applied to both small and medium-sized businesses that need a local analysis as well as enterprise companies that require a larger-scale view
- GIS systems can be integrated into your current software which allows you to manage data efficiently and be able to share it with a variety of stakeholders
Decision-makers have access to unprecedented amounts of geodata. Quarticle helps you break down silos and make sense of your data to enable effective decision-making and action. Reach out at [email protected] and let’s discuss how you can integrate GIS solutions and make a significant impact in your company.